Over the last two years or so, many organisations have upgraded or created their online presence. Many have moved to e-commerce, and many have made their main customer and media outlet a website and Social Media.
In tandem with this, the workplace has changed, as home and remote working becomes the norm, and customers demand access to corporate systems to monitor and place orders. The quality of online support has become a key differentiator.
In tandem with an increasing online presence has been the unfortunate side-effect of increases in the potential for cyber-attacks such as malware and network attacks. One such has been ransomware. As a result, Cyber Security Solutions have moved much higher on the IT Head’s priority list.
Improved cyber-security solutions have gone some way to stemming the increase in cyber-attacks, and indeed some reports have suggested that the number of ransomware attacks is falling.
What is Ransomware?

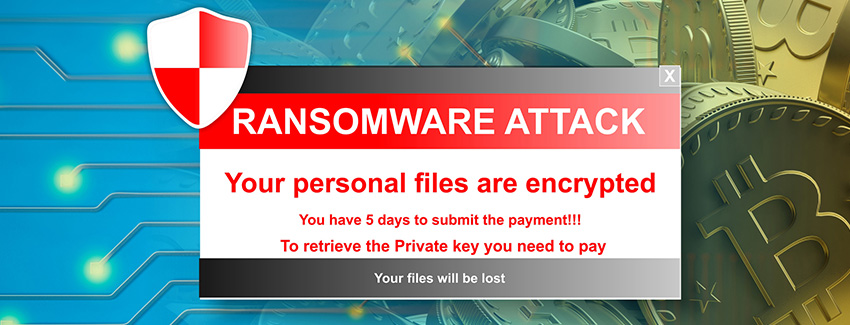
Ransomware is a type of malicious software, or malware, that encrypts the victim’s files or computer system, effectively locking them out of their own data. The attacker then demands payment, typically in the form of cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin, in exchange for the decryption key that can unlock the files.
Ransomware attacks can be targeted at individuals, businesses, and even government organizations. Attackers may use a variety of methods to spread ransomware, including phishing emails, malicious attachments, or exploiting vulnerabilities in software systems.
Once the ransomware is executed, it will typically display a message or pop-up window on the victim’s screen, informing them that their data has been encrypted and that they must pay the ransom to regain access.
It is important to note that paying the ransom does not guarantee that the attacker will provide the decryption key or that the files will be restored. Additionally, paying the ransom may encourage further attacks and can potentially fund other criminal activities. As such, it is recommended to have regular backups of important data and to implement strong security measures to prevent ransomware attacks.
Are Ransomware Attacks Decreasing?

Unfortunately, ransomware attacks are not decreasing, and in fact, they have been on the rise in recent years. According to a report by cybersecurity company SonicWall, there were over 304.7 million ransomware attacks globally in 2020, which represents a 62% increase from the previous year.
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly sophisticated, with attackers using new techniques such as double extortion, where they not only encrypt the victim’s data but also steal it and threaten to release it publicly if the ransom is not paid. Additionally, attackers are now targeting larger organizations and demanding larger ransom payments, with some recent attacks resulting in demands for millions of dollars.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also provided new opportunities for attackers, with many organizations shifting to remote work and potentially leaving their systems more vulnerable to attack.
In summary, ransomware attacks continue to be a significant threat, and it is important for individuals and organizations to take steps to protect themselves, such as implementing strong cybersecurity measures and regularly backing up their data.
How to Combat Ransomware

Before considering combat and recovery measures, there is one very important point to consider. Experience has shown that the only quick and secure way to recover after an attack is to drop all your systems to bare metal and reload a clean backup or system image from scratch.
Secondly, do not pay the ransom and report the attack to the appropriate authorities. You may or may not get a decryption key, and if you do receive one, it may or may not work in full or work only in part. Further, some keys are designed to leave a trojan behind, which can be reactivated by a remote command, reinfecting your system.
There are several steps that individuals and organizations can take to combat ransomware and reduce the risk of falling victim to an attack. Here are some of the most effective measures:
- Keep your software up to date: Regularly update your operating system, web browsers, and other software programs to ensure that you have the latest security patches and fixes.
- Use strong passwords: Choose strong, unique passwords for all your accounts and enable two-factor authentication wherever possible.
- Be cautious with email: Be wary of opening email attachments or clicking on links from unknown or suspicious sources. Use an email filtering service to block spam and phishing emails. Make sure your staff know what to do if they suspect an infected email.
- Backup your data: Regularly backup your systems and data to an external hard drive, cloud storage service, or another secure location. Make sure you have clean system images backed up. As noted above, this will help you restore your systems and data in case of a ransomware attack.
- Install security software: Install and use reputable antivirus and anti-malware software on all devices to detect and block ransomware and other malicious software.
- Train your employees: Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices, including how to recognize and avoid phishing attacks and suspicious emails.
- Have a response plan: Develop a response plan for dealing with a ransomware attack and include it in your Business Continuity Plan. It will show steps for isolating infected systems, notifying law enforcement, and communicating with stakeholders.
By implementing these measures, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to a ransomware attack and mitigate the potential impact of an attack.
